
Updated: Mar 23
We’ve all heard it, in the news and in the ads: 5G is here.
But what is 5G, exactly? 5G, as in the fifth generation of mobile technology, promises faster speed, better reliability, and wider coverage. But the benefits of 5G come with some very important caveats and shortcomings. Naturally, these are the things which don’t make it into the ad campaigns or the slogans on the mobile carriers’ websites.
But not to worry: we’re here to separate the reality from the advertising for you. First, we have to get just a bit technical.
The Different Flavors of 5G
When carriers advertise 5G, they often allude to an ultra-fast network that will revolutionize our daily lives. As for now, this is not necessarily true. For example, what you won’t hear from carriers is that there are two main varieties of what is considered 5G data coverage today: Sub-6 and mmWave
You’re probably wondering, what the heck do these terms mean and how do they differ? Luckily, it’s only a little complicated: the terms describe services in different frequencies in the airwaves. And frequencies are measured in Gigahertz (GHz).
Sub-6: The “Better than 4G” 5G
Sub-6 just means mobile data with frequencies below 6GHz.
This is what most users are going to experience when they experience 5G, because sub-6 for the time is much more widespread. sub-6 is generally a bit faster than what people experience with LTE; for the user, this means that download and upload speeds could be anywhere from 20% to 6x faster than 4G LTE.
These speeds are quicker on paper, but they likely won’t show much of a detectable difference to the user. That’s because sub-6 and 4G LTE essentially share the same network. In fact, our tests show that Sub-6, while usually faster, can sometimes actually be slower than 4G, depending on the type of phone and the location.
From what it appears, the Sub-6 network will be included in your plan. However, you probably won’t be experiencing anything much faster or better than 4G.
mmWave: The “Real” 5G
In contrast to sub-6, mmWave 5G is ultra-fast. That’s because it uses higher frequencies ranging from 24GHz to 40GHz. It’s an enormous jump up in speed from sub-6 or current 4G LTE speeds. mmWave is the “real 5G” you’ve seen in the ads.
It’s so fast, in fact, it’s possible you don’t have any applications on your phone that really need it to work well. Beyond whether you’d actually use the speed, though, mmWave comes with certain shortcomings.
For one, mmWave 5G has an extremely short range. This means that in order to use the technology, you would have to be within a block of a 5G tower, or possible within line of sight. Additionally, as of now, it is only available in certain urban/congested areas.
As of December 2020, Android Authority listed only 6 cities in the entire country where t-Mobile users could get mmWave, for example. Verizon lists 55 cities, but beware: only the most central, congested areas of those cities actually have access to the short-range technology. Check out this map of Verizon 5G coverage in Philadelphia, for example:
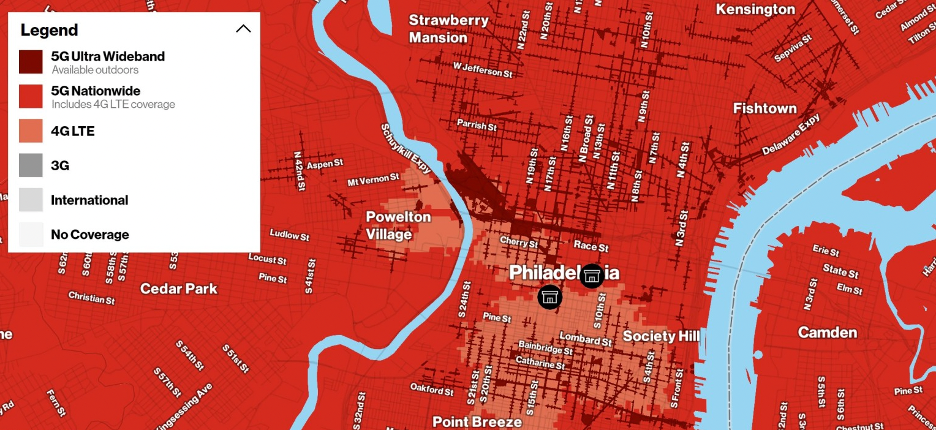
Only the ultra-dark red areas have the higher Gigahertz 5G coverage. As you can see, it’s entirely possible to be on a street and get it, but go into a building on that same street and not get it (map via PC Magazine)
This limits “real” 5G’s usability for many people who live and work in suburban or rural areas, and even urban ones.
The Cost of 5G
If you thought “the real 5G” would come without a cost, you’re wrong. For example, Verizon is charging their customers $10 extra per month to use their “5G Ultra Wideband” services. Surprising, right? Over time, and as new technology is introduced to the market, however, we predict that some of these costs could be absorbed.
While buying a 5G phone today may be future proofing, until the network is more widespread consider carefully whether it’s worth spending the extra money on a phone that may only be in your fleet for a few years. After all, today most 5G phones are far from the cheapest option you can buy on an enterprise plan.
The Future
The real 5G will eventually bring more speed and reliability. 5G will be able to handle a record number of devices, and its implementation has the possibility to increase efficiency in many areas of business. For instance, the ultra-low latency that 5G provides could revolutionize telehealth as we know it.
However, as with any newly introduced technology, there’s still a long way to go and there are a few costs that need to be considered. As of now, the ultra-fast 5G that we desire is just an add-on feature that isn’t practical for all users. Despite this, there is still a lot of growth yet to see from 5G, meaning that it is imperative to prepare for a 5G world even if sub-6 and mmWave technologies may not be worth it yet.
Here at LINQ, we want to make sure that you get and understand what you need from 5G. For this reason, we will continue to update this page every quarter to keep you up to speed with all things 5G.
For more information about 5G and its implications for you and your business, please contact [email protected].



