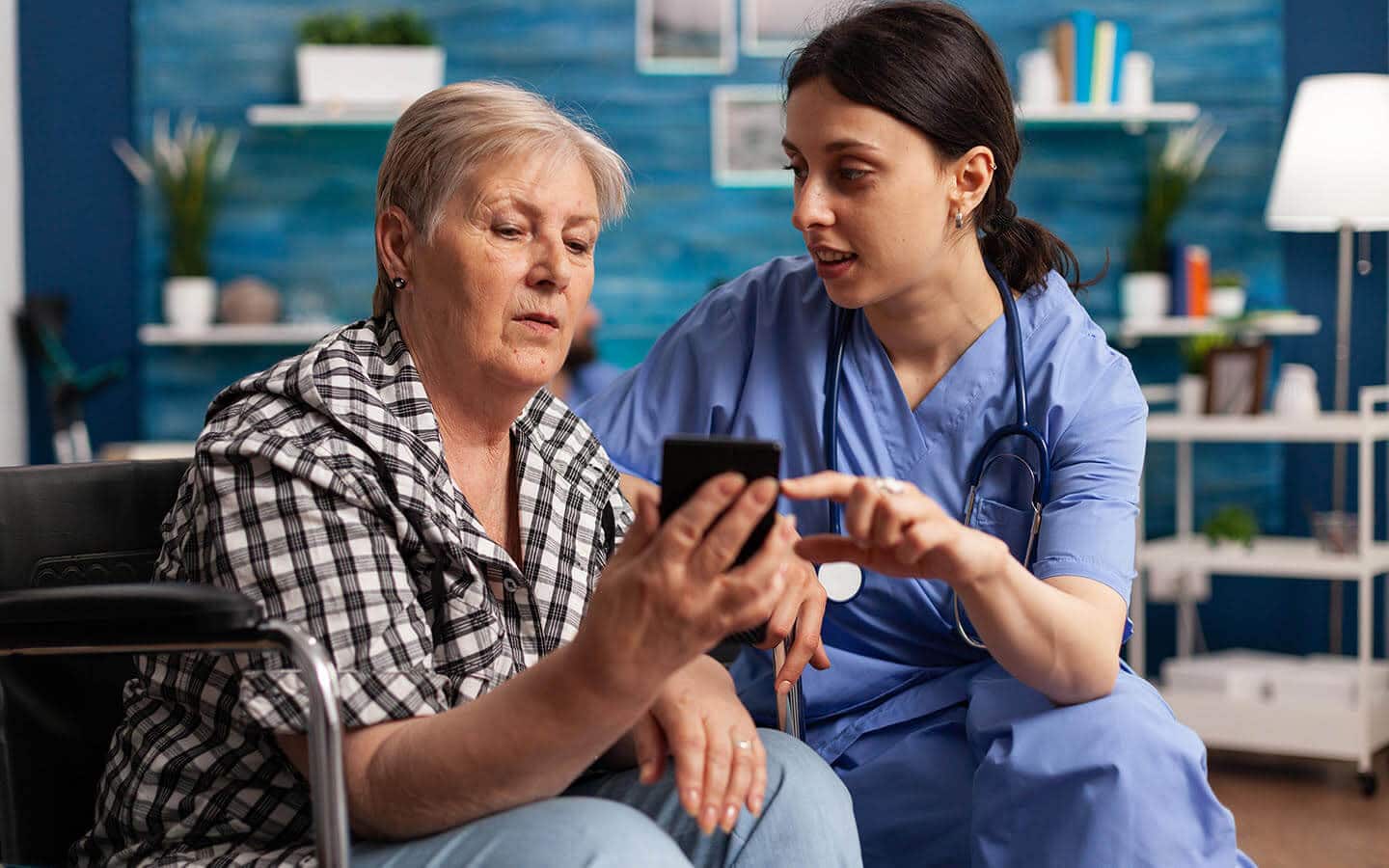
Advances in healthcare technology have expanded the types of care that patients can receive at home, leading to improvements in patients’ well-being and reductions in the overall costs of care. At-home services are evolving for patients with chronic conditions; patients who need nursing care, such as ostomy support; individuals needing physical, occupational, and speech therapy; as well as seniors.
A McKinsey analysis found that home care is on the rise and represents a win–win for patients and providers. Patients enjoy the comfort and familiarity of their home, together with higher quality of care. Healthcare facilities, physician groups, and other stakeholders derive more value through care because it costs less and can lead to better outcomes.
Between 2016 and 2019, physicians’ use of and interest in remote care tools increased significantly, according to a 2020 study from the American Medical Association. For 60 percent of physicians, the ability to provide care remotely is an important driver for digital health adoption. The pandemic, with its surge in virtual care, has prompted a further rethinking of at-home possibilities.
Meanwhile, Baby Boomers are aging — members of this generation will be 65 and older by 2030 — and they are more likely to want to age in place. They’ll do so, in part, by taking advantage of home healthcare services.
Together, these trends are elevating the role of the mobile device within home healthcare. Cell phones and tablets are now integral to care delivery at home, improving efficiency, communication, and outcomes.
Mobile Devices: A vital link between patient and provider
Whether patients are in short-term recovery or long-term management of chronic conditions, their mobile devices play a critical role in keeping caregivers and care team members connected. When patient conditions make it difficult to travel to a hospital or doctor’s office, mobile devices ensure they don’t miss out on the support they need.
Through quick check-ins and in-depth telehealth sessions, patients can share information, ask questions, and maintain communication — key ingredients for timely, up-to-date care management. Mobile device apps help to improve medication adherence, which can be a challenge for patients once they leave the hospital. In addition, at-home patients are less likely to be exposed to illnesses that may lead to hospital-acquired infections — these infections affect one out of every 25 hospital patients.
When patients’ family members play a role in their care, mobile devices can streamline the process of coordinating home visits, appointments, medications, and other critical tasks. Often, patient caregivers are spouses and adult children who also work full-time and care for other family members. The ease and flexibility of being able to conduct care-related management on a mobile device can ease their potential burden.
Mobile devices also increase the likelihood that everyone will stay in the loop and on the same page. That’s essential when home healthcare might involve rotating clinicians who visit the home, as well as clinicians who primarily consult with patients from their offices.
Supporting Quick, Fact-Based Decision Making
Clinicians are extremely busy and need key information to make care decisions fast. Mobile devices provide instant access to critical information such as patient records; test and lab results; applications for remote patient monitoring devices; platforms that facilitate collaboration among clinicians; and communication services, such as text, email, and video.
In hospital settings, many providers have adopted clinical collaboration platforms, including secure messaging, to streamline colleagues’ communication and access to information. Mobile devices, by providing remote access to these tools, bring the same benefits into home healthcare: increased efficiency, a reduction in manual processes, and a more user-friendly approach to care coordination.
For instance, clinicians can use their mobile devices to document shift change information, rather than relying on manual processes that can be cumbersome and prone to error. Mobile device cameras make it easy to document patients’ conditions and obtain input from remote care team members.
Together, improvements like these facilitate more holistic decision-making, as well as faster, more accurate diagnoses — two factors that can significantly improve patient outcomes.
Enabling Critical Alerts and Interventions
Mobile devices facilitate the collection of data and the use of algorithms to monitor patients remotely and provide early-warning alerts.
Via text, email, or app, patients answer a series of questions that give clinicians valuable insight about their status. When the algorithm detects that patients’ responses indicate a need for medical attention — for instance, a change in symptoms suggests that a disease is progressing — it sends an alert to clinicians on their mobile devices.
A 2021 study published by the Journal of the American College of Cardiology found that remote patient monitoring, in concert with analytics, reduced the overall resources that were required to attend patients, while leading to more actionable interventions.
Remember: HIPAA compliance is critical for care providers using mobile devices
With increased connectivity comes increased risk. As more providers adopt mobile solutions to support care delivery, they must ensure HIPAA compliance to keep Protected Health Information (PHI or ePHI) safe from compromise. Every gateway to a healthcare computing system, whether that be a mobile phone, tablet, or laptop, is a vulnerability that could expose sensitive health information to the wrong people.
According to the US department of Health and Human Services (HHS), health care providers, other covered entities, and business associates may use mobile devices to access electronic protected health information (ePHI) in a cloud as long as appropriate physical, administrative, and technical safeguards are in place to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the ePHI on the mobile device and in the cloud, and appropriate BAAs are in place with any third party service providers for the device and/or the cloud that will have access to the ePHI.
Looking ahead
The number of healthcare solutions designed for at-home care continues to expand, spurred by patients’ growing demand, providers’ need to reduce costs, and ongoing developments in healthcare technology. In the process, the role of mobile devices will also continue to evolve, helping to improve patient outcomes, ease the burden on caregivers, and support the essential work of home healthcare clinicians.